안녕하세요 보나에요~ 전에꺼에 이어서 해볼께요!
(1)을 보시고 싶으면 https://bonahbruce.tistory.com/76
여기로 들어가보세요!
kubernetes에 jupyter container 띄우기 ( azure 활용)
안녕하세요 본아에요~ 오늘은 portal.azure.com의 vm 안에서 aks, acr등을 활용하여 jupyter notebook을 올리는 작업을 한번 진행해 보겠습니다.(부족한 점이 많아요) 1. portal azure 로그인 후, 리소스 그룹을..
bonahbruce.tistory.com
전에거에서는, persistent volume이 없어서, jupyter에서 데이터분석을 열심히~ 했어도
기록이 남아있지 않아요.... 말짱 도루묵.... 인거죠
왜냐면 k8s는 기본적으로 stateless한 클러스터를 구축하기 때문에
자기가 사용할 volume을 미리 만들어서 붙여주거나, (static)
아니면, pod를 띄우면서 dynamic하게 생성하는 방법이 있어요!
동적으로 하는거는 아직 제가 서툴러서... 우선 제가 구현해본 static 버전으로 설명을 드려볼게요!!
우선 저는 public cloud 중 azure를 사용하고 있어요~!
그래서! 사용할 storage(창고)를 위해 storage account를 개설할거에요!

요렇게 생겨먹은것을 생성한 뒤,

access keys 부분으로 들어가셔서, key1 또는 key2를 복사해주세요
그 후,
kubectl create secret generic fileshare-secret --from-literal=azurestorageaccountname=bonahstorage --from-literal=azurestorageaccountkey=<key1입력> -n jupyter이런식으로 secret을 생성해주면 됩니다!
여기서
fileshare-secret = secret의 이름
bonahstorage = Azure에 있는 storageaccount 이름
<key1입력> = key에 있는 엄청 긴 값(여기에서 <>는 제거하고 넣으셔야되요)
자,,
그렇게 생성을 하고 나면
이제 yaml 파일 두개를 생성해야되요!
1. pv
pv는 이제 persistent volume이라고 해서, 실제 존재하는 pv를 명시하는 부분이고
2. pvc
pvc는 이제 요청을 하는거에요. 나 요런 저장공간을 갖고있는 pv를 붙이려고해!!
그러면 pv에 있는 저장소중 pvc에서 요청한 것에 충족되는 pv를 불러와서 inbound하게 됩니다. (제가 이해한바론..)
pv.yaml파일은 다음과 같이 생겼어요
kind: PersistentVolume
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: fileshare-pv
labels:
usage: fileshare-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 10Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
azureFile:
secretName: fileshare-secret
shareName: bonah
readOnly: falsepvc.yaml파일은 다음과 같이 생겼어요
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: fileshare-pvc
# Set this annotation to NOT let Kubernetes automatically create
# a persistent volume for this volume claim.
annotations:
volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: ""
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
selector:
matchLabels:
usage: fileshare-pv두 yaml 파일을 모두 apply 해주세요!
kubectl apply -f pv.yaml -n jupyter
kubectl apply -f pvc.yaml -n jupyter그 후, 다시 jupyter.yaml을 deploy 하면 됩니다! 아 ! 그전에!
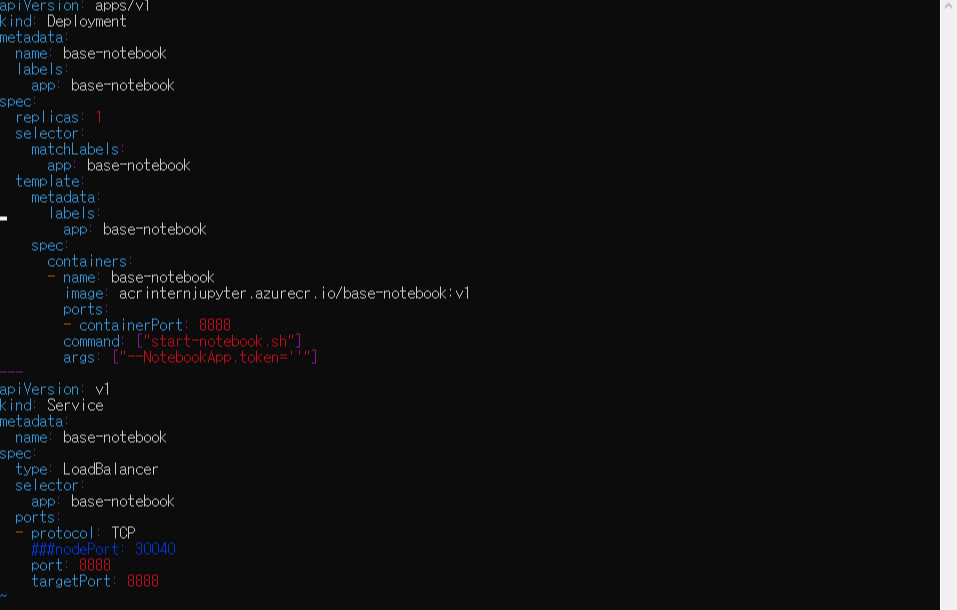
jupyter.yaml에서 deployment 부분을 살짝 추가를 해야 하는 부분이 있습니다.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: base-notebook
labels:
app: base-notebook
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: base-notebook
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: base-notebook
spec:
volumes:
- name: azure
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: fileshare-pvc
containers:
- name: base-notebook
image: acrintern.azurecr.io/base-notebook:v1
ports:
- containerPort: 8888
command: ["start-notebook.sh"]
args: ["--NotebookApp.token=''"]
volumeMounts:
- name: azure
mountPath: "/home/jovyan/work"기존 yaml 형식에서 모두 같지만, persistentVolumeClaim이라는 부분이 새로 추가되었을거에요!
pv를 요청하는 pvc를 저희가 만든 pvc.yaml에서 fileshare-pvc라고 metadata name을 설정해놓았어요!(위에 보시면됩니다) 그래서 그 pvc를 불러오는거에요! 나 fileshare-pvc 레이블이 있는 pvc.yaml파일에서 생성한 그 claim을 쓸거야! 이런느낌입니다.
그리고 실행하면 pv가 붙은 jupyter notebook이 탄생하게 됩니다~~ 짝짝짝
다음에는, 저희가 loadbalancer를 사용해서 외부에서 접근가능하게 해준것을,
azure를 사용하면 제공해주는 domain name으로 변경해서 사용하는, 간편한 방법을 이용해볼게요!!
다음에 만나욥!
'IT > Kubernetes' 카테고리의 다른 글
| helm을이용해 k8s에 kafka 설치하기! (1) | 2020.08.11 |
|---|---|
| helm 설치 (0) | 2020.08.11 |
| kubernetes multiple cluster일때 cluster 옮기는 방법 (0) | 2020.08.03 |
| k8s 정리 (0) | 2020.07.31 |
| kubernetes에 jupyter notebook 띄우기 (1) (0) | 2020.07.15 |